Riddles For Adults offer a captivating blend of logic, wordplay, and lateral thinking, challenging minds and sparking creativity. This exploration delves into the diverse world of adult riddles, examining their construction, psychological impact, and prevalence in popular culture. We’ll uncover the cognitive processes involved in solving these brain teasers, and explore how they can enhance problem-solving skills and critical thinking.
Riddles for adults offer a stimulating mental workout, perfect for downtime after a long day. Finding the ideal long-term rental can be just as challenging, and if you’re searching for a relaxing escape, consider checking out the available options on sites like maui long term rentals craigslist before settling in to solve some brain-teasers. Once you’ve found your perfect Hawaiian haven, those riddles will seem even more appealing.
From easy word puzzles to complex logic challenges, we’ll analyze various riddle types, providing examples across different difficulty levels and themes. We’ll also examine the art of crafting effective riddles, including the use of puns and multi-step logical deductions. The role of visual elements in enhancing riddle complexity will be discussed, alongside the impact of context on interpretation and difficulty.
Finally, we’ll explore the use of riddles in literature, film, and games, and how they contribute to suspense and intrigue.
Types of Riddles for Adults
Riddles for adults differ significantly from those designed for children, exhibiting increased complexity, nuanced wordplay, and a broader range of themes. They often require more abstract thinking, logical deduction, and a deeper understanding of language and culture. This section categorizes adult riddles by difficulty and theme, highlighting the key distinctions.
Riddle Difficulty and Theme Examples
The complexity of a riddle is influenced by factors like wordplay, the number of logical steps required, and the breadth of knowledge needed for a solution. The following table illustrates examples across varying difficulty levels and themes:
| Difficulty | Riddle | Answer | Theme |
|---|---|---|---|
| Easy | What has an eye, but cannot see? | A needle | Wordplay |
| Medium | What has to be broken before you can use it? | An egg | Lateral Thinking |
| Hard | What is full of holes but still holds water? | A sponge | Logic |
| Medium | What is always in front of you but can’t be seen? | The future | Abstract Concept |
Further examples based on different themes include:
- Wordplay: “What has no voice but can still tell you stories?” (A book)
- Logic: “If a train leaves Chicago traveling 60 mph and another train leaves New York traveling 70 mph, which train is closer to New York?” (The train leaving New York)
- Lateral Thinking: “A man is found dead in a field. He has a pack on his back. There are no signs of violence. What happened?” (His parachute failed to open)
- Knowledge-Based: “What is the capital of Australia?” (Canberra)
Adult riddles often incorporate more sophisticated vocabulary, ambiguous phrasing, and require a broader base of knowledge compared to children’s riddles, which tend to be more straightforward and reliant on simple wordplay or easily observable characteristics.
Crafting Effective Riddles for Adults
Constructing engaging and challenging riddles requires careful consideration of structure, word choice, and the desired level of difficulty. The following examples illustrate different techniques.
Designing Riddles: Profession, Pun, and Logical Deduction
Here are examples demonstrating the crafting of riddles with specific characteristics:
- Profession-Based Riddle: “I wield a gavel, maintain order, and preside over justice. What am I?” (A judge)
- Pun-Based Riddle: “What do you call a lazy kangaroo?” (A pouch potato)
- Multi-Step Logical Deduction Riddle: “Three friends – Alex, Ben, and Chloe – each have a different favorite color: red, blue, and green. Alex doesn’t like red. Ben’s favorite color is not blue. What is Chloe’s favorite color? (To solve this, use the process of elimination: Since Alex doesn’t like red and Ben doesn’t like blue, and there are only three colors, Chloe’s favorite color must be green.)”
Creating a challenging riddle involving multiple steps of logical deduction involves starting with a core concept, then layering in additional clues and red herrings to increase the difficulty. The solution should be logical and achievable, but require careful consideration of all the presented information.
The Psychology of Riddles: Riddles For Adults
Solving riddles engages several cognitive processes, including working memory, problem-solving skills, and creative thinking. Understanding these processes helps in crafting effective and engaging riddles.
Cognitive Processes and Problem-Solving Strategies, Riddles For Adults

Source: quillwords.com
The cognitive processes involved in solving riddles include:
- Pattern Recognition: Identifying recurring elements or structures in the riddle’s wording or clues.
- Deductive Reasoning: Using logical steps to eliminate possibilities and arrive at a solution.
- Lateral Thinking: Considering unconventional or unexpected approaches to problem-solving.
- Memory Retrieval: Accessing relevant knowledge or information from long-term memory.
Problem-solving strategies vary depending on the riddle type. Wordplay riddles rely heavily on linguistic knowledge and creative thinking, while logic riddles emphasize deductive reasoning and analytical skills. Lateral thinking riddles require a shift in perspective and the ability to consider unusual solutions.
Elements that contribute to a riddle’s engagement and memorability include clever wordplay, unexpected twists, a satisfying “aha!” moment upon solution, and relevance to the solver’s experiences or knowledge base.
Riddles in Popular Culture
Riddles are frequently used in various forms of popular culture to add intrigue, challenge the audience, and advance the narrative. Their use varies widely, from simple puzzles to complex plot devices.
Examples of Riddles in Books, Movies, and Games
| Source | Riddle | Answer | Analysis of its Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|
| The Hobbit by J.R.R. Tolkien | What has an eye, but cannot see? | A needle | Simple yet effective in establishing the character of Gollum and hinting at his obsession with riddles. |
| The Da Vinci Code by Dan Brown | (Numerous complex riddles involving historical artifacts and codes are present throughout the book) | Varying answers depending on the specific riddle. | Riddles are integral to the plot, driving the narrative and creating suspense. |
| The Saw movie franchise | (Various deadly, complex riddles and traps are used throughout the series) | Varying answers depending on the specific trap. | Riddles and traps heighten the tension and create a sense of impending doom. |
In storytelling, riddles can create suspense by delaying the revelation of crucial information or by presenting challenges that the characters must overcome. The ambiguity inherent in many riddles can also add layers of meaning and interpretation.
The context of a riddle significantly influences its interpretation and difficulty. A riddle’s meaning can shift based on the surrounding narrative, the characters involved, and the overall tone of the story. A riddle presented in a playful context might be viewed differently than one presented in a serious or ominous setting.
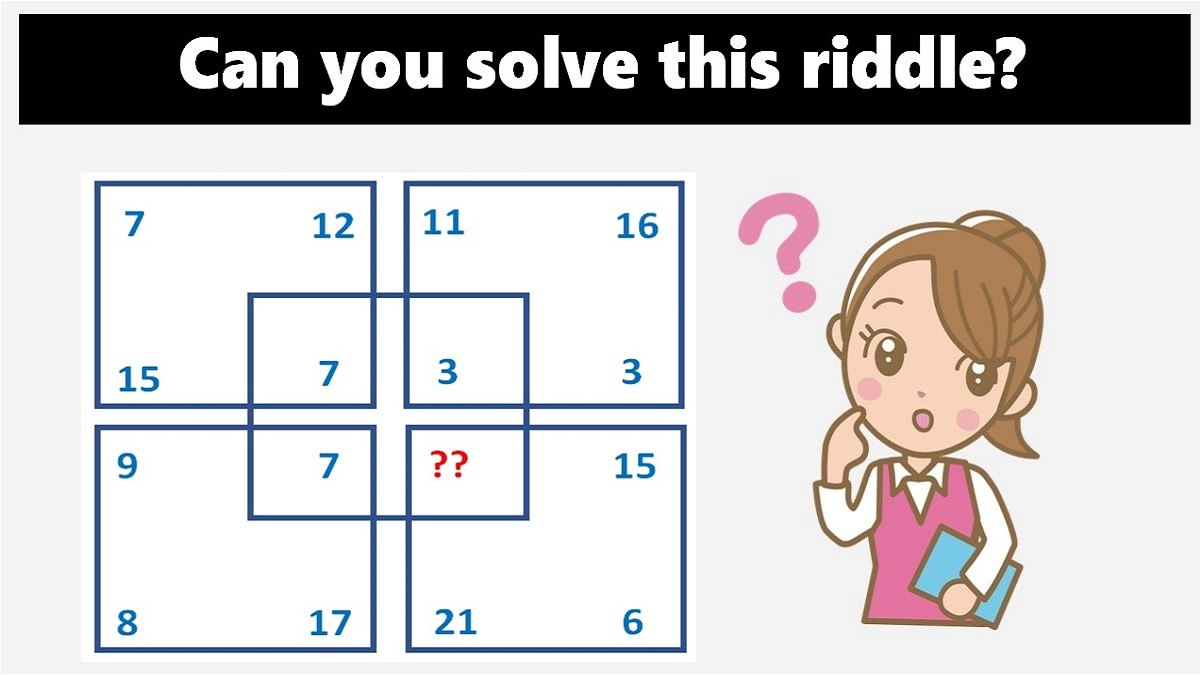
Visual Riddles for Adults
Visual riddles, combining images and text, present a unique challenge, demanding both visual interpretation and logical reasoning. The addition of visual elements can significantly enhance the complexity and engagement of a riddle.
Visual Riddle Examples
Here are some examples of visual riddles with descriptions:
- Riddle 1: Depict a clock showing 8:
20. The riddle text: “What time is it when the clock strikes thirteen?” The visual element emphasizes the impossible nature of a clock striking thirteen, leading to the answer: It’s time to get a new clock. - Riddle 2: Show an image of a partially submerged iceberg. The riddle text: “What is bigger than you, but you can only see a small part of it?” The visual element highlights the hidden nature of most of the iceberg, leading to the answer: An iceberg, or more generally, a problem.
- Riddle 3: Show a picture of a maze with a clear path to the exit. The riddle text: “What is the most efficient way to get from point A to point B?” The visual element presents a clear solution, but the riddle can be open to different answers depending on the interpretation.
Visual elements enhance the complexity of riddles by adding layers of information that require visual processing and interpretation, in addition to textual understanding. This multi-modal approach engages different cognitive processes and increases the overall challenge.
Riddles and Problem-Solving Skills
Solving riddles is a valuable exercise that enhances cognitive skills, particularly critical and creative thinking. The act of deciphering riddles translates into broader problem-solving abilities.
Enhancing Problem-Solving Abilities Through Riddles
Source: jagranjosh.com
Solving riddles improves critical thinking by:
- Developing analytical skills: Riddles often require breaking down complex information into smaller, manageable parts to identify patterns and relationships.
- Improving deductive reasoning: Solving many riddles involves using logical steps to eliminate incorrect answers and arrive at the correct solution.
- Enhancing pattern recognition: Identifying recurring elements or structures in the riddle’s wording or clues is crucial for solving many riddles.
The connection between riddle-solving and creative thinking lies in the need to think outside the box. Many riddles require unconventional approaches and a willingness to consider unusual possibilities.
In educational settings, riddles can be used to enhance problem-solving abilities by:
- Introducing challenging scenarios: Riddles provide engaging contexts for practicing critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
- Promoting collaborative learning: Working together to solve riddles fosters teamwork and communication skills.
- Encouraging creative thinking: Riddles that require lateral thinking promote innovative and unconventional solutions.
Closing Notes
The world of riddles for adults is a rich and rewarding one, offering a stimulating mental workout and a glimpse into the fascinating intersection of language, logic, and creativity. Whether you’re a seasoned riddle solver or a curious newcomer, the ability to craft and solve these brain teasers offers significant benefits, sharpening critical thinking and problem-solving skills while providing endless entertainment.
The exploration of riddles, from their simple beginnings to their complex applications, ultimately reveals their power to challenge, intrigue, and delight.
